Capnography
Capnography
- Capnography is a non-invasive method of monitoring a graphical display of CO2 throughout the respiratory cycle.
- Capnography directly reflects the elimination of CO2 by the lungs (ventilation).
- Capnography has been the standard of care for monitoring patient safety during anesthesia because it provides a quick and reliable method for detecting life-threatening conditions like malposition of tracheal tubes, ventilatory failure, circulatory failure, and defective breathing circuits.
Why use Capnography?
- Pulse oximetry monitoring is not enough to ensure patient safety.
- The patients CO2 will rise well before a fall in SpO2, especially when supplemental oxygen is administered.
- In addition, capnography can provide information about pulmonary perfusion, alveolar ventilation, and respiratory patterns.
Types of capnograph
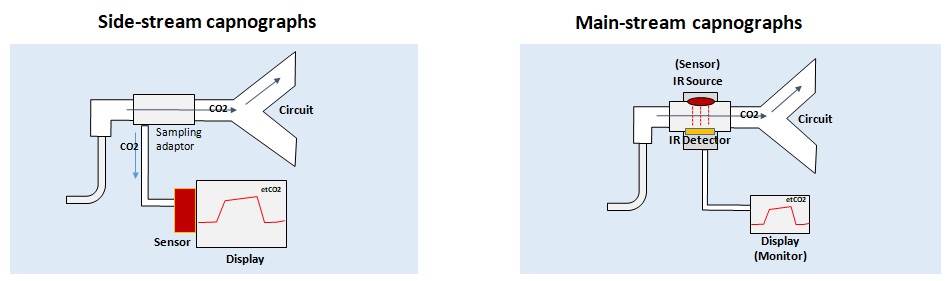
Side-stream capnographs
- Sensor is located in the main unit and CO2 is aspirated via a sampling tube connected to a T-piece adapter located between endotracheal tube and breathing circuit.
- Tiny pump aspirates gas samples from the patients airway through a capillary tube into the main unit.
Main-stream capnographs
- CO2 sensor located between endotracheal tube and breathing circuit.
- A lightweight infrared sensor is then attached to the airway adapter. The sensor emits infrared light through the adapter windows to a photodetector typically located on the other side of the airway adapter. The light which reaches the photodetector is used to measure ETCO2.
Side-stream Capnographs
Advantages
- Easy to connect
- No problems with sterilization
- Can be used in awake patients
- Easy to use when patient is in unusual positions such as in prone position
- Can be used in collaboration with simultaneous oxygen administration via a nasal prong
- Monitoring of non-intubated subjects, as sampling of the expiratory gases can be obtained from the nasal cavity using nasal adaptors.
Disadvantages
- Delay in recording due to movement of gases from the ET to the unit
- Sampling tube obstruction
- Water vapor pressure changes affect CO2 concentrations
- Pressure drop along the sampling tube affects CO2 measurements
- Deformity of capnograms in children due to dispersion of gases in sampling tubes
Main-stream Capnographs
Advantages
- No sampling tube
- No obstruction
- No affect due to pressure drop
- No affect due to changes in water vapor pressure
- No pollution
- No deformity of capnograms due to non
- dispersion of gases
- No delay in recording
- Suitable for neonates and children
Disadvantages
- Contrary to the earlier versions, the newer sensors are light weight minimizing traction on the endotracheal tube
- Long electrical cord, but it is lightweight
- Facial burns have been reported with earlier versions. This has been eliminated with newer sensors
- Sensor windows may clog with secretions. However, they can be replaced easily as they are disposable
- Difficult to use in unusual patient positioning such as in prone positions.
- The newer versions use disposable sensor windows thereby eliminating sterilization problem