Catheter
- What is catheter?
- Type of catheter?
- What is a Catheter made up of?
- Catheter size.
- Curve selection factors.
- Different catheter shapes.
Catheter
- Late Latin, from Greek:
- KATHETER, came from KATHIENAI
- kathe- to send down: kat-, kata- , cata- + hienai - to send.
- A catheter is a thin plastic tube that can be inserted into a blood vessel(artery) through a small incision in the skin to deliver diagnosis and treatments inside that blood vessel.
- For angiography, x-ray dye(contrast material) flows through the catheter into the arteries so the images of any blockages in the artery are captured using a small dose of X-ray.
- During angioplasty, a balloon or another device is mounted on the catheters tip and guided to the narrowed section of the artery over a guidewire. (to reopen the artery for blood flow)

Catheters can be classified into these 2 groups

- Guiding catheters are more stiff & firm than diagnostic catheters because guiding catheters are supposed to carry Balloon catheters, PTCA wires and stent delivery system.
- Good Tractability and Pushability
What is a Catheter made up of?
Materials:
- For the construction of catheter, a range of polymers including
- silicone rubber latex
- thermoplastic elastomers
- Because of:
- inert and unreactive to body fluids and a range of medical fluids
-
Silicone is one of the most common choices
-
- inert and unreactive to body fluids and a range of medical fluids
- Catheter (materials):
- Polyvinylchloride (PVC)
- Polyethylene (PE)
- Fluoropolomers (PTFE) (TEFLON)
- Polyurethane (PUR)
- Silicone (SI)
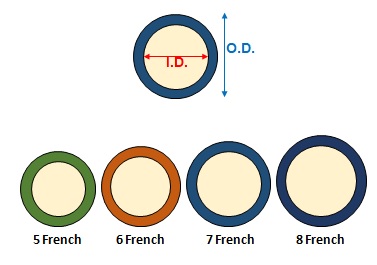
Catheter size
- Catheters are named by their O.D. in French
- 1 French = 0.33 mm
- For each size – I.D. (Inner Lumen) could be vary depending on manufactures.
- Historically, 8F guides were necessary to deliver devices because of their larger internal lumens.
- Current 6-7F catheters have internal lumens just as large as the previous generation 8F catheters.

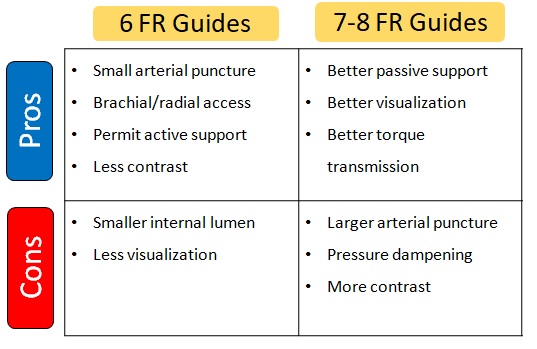
Compare of 6FR vs. 7-8FR
Catheter Parameters
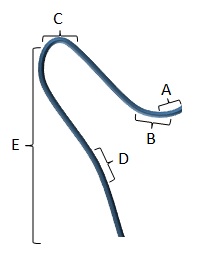
Catheter Selection: Select a catheter that points in the general direction you wish to travel.
- Tip Length
- Primary Curve
- Secondary Curve
- Tertiary Curve
- Catheter Length: Shorter length catheters (50 cm), Mid length catheters (65 cm), Longer length catheters (100-125 cm)
Curve selection factors
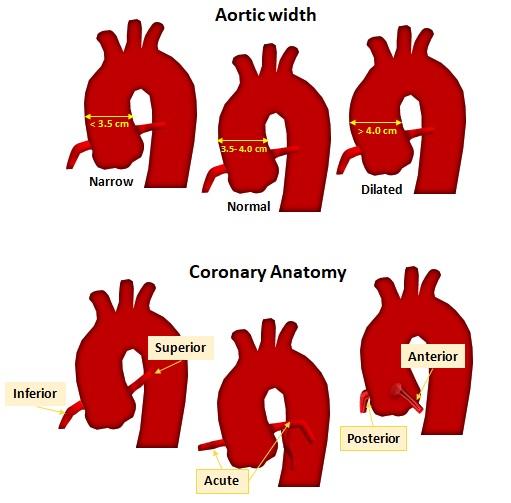
- Aortic Width
- Coronary Anatomy
- French Size
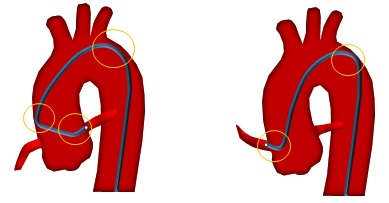
- Active vs. Passive Support
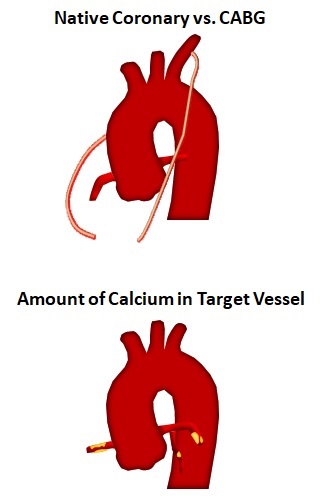
- Native Coronary vs. CABG
- Amount of Calcium in Target Vessel
- Radial vs. Femoral approach
Aortic width and Coronary Anatomy
French Size
Active vs. Passive Support-Backup Support
Native Coronary vs. CABG
Amount of Calcium in Target Vessel
Radial vs. Femoral approach
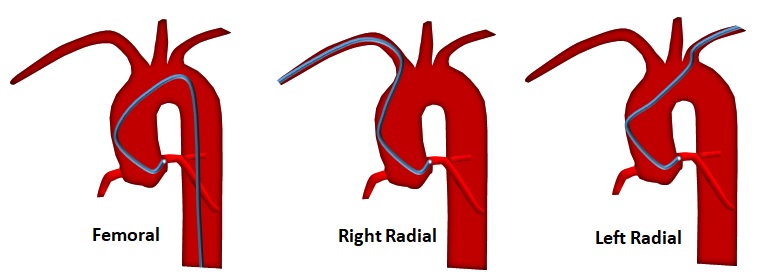
3 most frequently used catheter types
 F P T D.jpg)