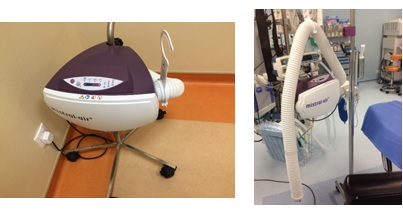
Convective Air Warming System
Temperature Management
Main part of the Temperature Management is Perioperative Hypothermia.
- A cooling down of patients undergoing a surgical procedure due to the physiological and environmental circumstances.
The regulation of the body temperature
- The balance between heat absorption and heat loss causes the body temperature to stay constant at the same temperature. The hypothalamus and thermo-receptors monitor and control this thermo-regulation.
- Thermo-receptors are located in the skin and in the hypothalamus itself. All information from the receptors are transferred to the hypothalamus.
- If the preset temperature value is under or overachieved by 0.4 degrees, correction mechanisms are activated until the pre set figure is reached again.
- A temperature increase is mostly generated be shivering, vasoconstriction….
- A temperature decrease via sweating, vasodilatation….
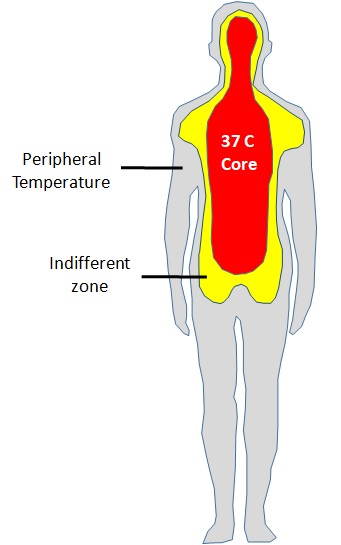
Body Temperatures
- Core Temperature (That temperature of the body which is least impacted by external factors or environment. Considered the true temperature of the body)
- Central body temperature near the hypothalamus.
- Skin/ Peripheral Temperature
- Indifferent zone :
- is the area between the core and skin/peripheral temperature.

OR Related Circumstances
- Usually the heat production is reduced by 30% during a surgical procedure.
- On average, the body temperature decreases by 1.6 degrees in the first hour due to a vasodilatation. Afterwards, the temperature decreases by about 1 degree per hour.
There are some factors that decrease a patient’s body temperature during surgery.
- Cold anesthesia gases
- Semi open breathing circuit
- Cold I.V. liquid
- Cold irrigation liquid
- Open body cavities
- Low room temperature
- Cold OR-table
- Skin disinfecting
- Air condition
- Reduced isolation

Hypothermia Related Side Effects
1.Metabolism and Oxygen
- Reduced metabolism and oxygen-transport
2.Heart/ Peripheral Vascular System
- Increase risk of heart attack
- Increased volume per heart beat and arterial pressure
3.Blood/ breathing
- Reduced plasma-volume and defense system
- Disturbed perfusion and blood coagulation
4.Kidney and Gastrointestinal Area
- Disturbed kidney function
- Reduced re-absorption of Glucose and Sodium

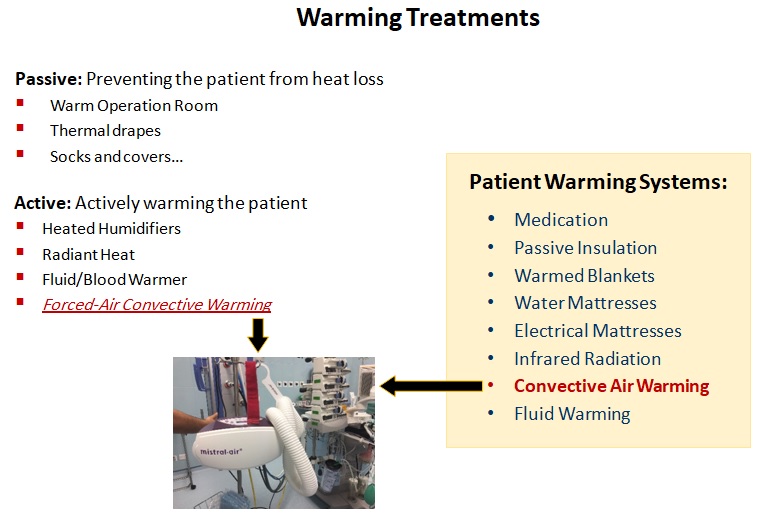
Warming Treatments
Passive: Preventing the patient from heat loss
- Warm Operation Room
- Thermal drapes
- Socks and covers…
Active: Actively warming the patient
- Heated Humidifiers
- Radiant Heat
- Fluid/Blood Warmer
- Forced-Air Convective Warming
Patient Warming Systems:
- Medication
- Passive Insulation
- Warmed Blankets
- Water Mattresses
- Electrical Mattresses
- Infrared Radiation
- Convective Air Warming
- Fluid Warming
Pros and Cons
- Electrical heat mattresses
- Reduced contact area
- Electrical wiring disturbs the x-ray
- Burning risk
- Water mattresses
- Reduced contact area
- Burning risk
- Convective Air Warming
- One of the most effective warming treatment on the market.
- Up to 70% of the body-surface can be used as contact area.
- No burning risk
Introduction to Convective Air Warming
- Warming units(Blower) filter air and then force warm air through a disposable blankets, which cover patients before, during and after surgery.
A forced air warming device comprises
- A Controller (Blower)*
- A Compatible Disposable Forced Air Warming Blanket*
*The controller is reusable with a life expectancy of several years. It contains the following components:
- Electric motor and fan
- Electric heating element
- Thermostat
- Air filter
- Hose
*All forced air warming blankets are intended for single-patient use and are disposable. Every manufacturer have their owe blanket design.
Blankets are designed to use pressure points on the patient’s body to prevent heat from reaching areas at risk for pressure sores or burns.
How forced air warming devices work?
- Firstly, the user connects the hose nozzle to the compatible, disposable blanket.
- In operation, the fan draws in air through the filter and the heating element heats the air to a selected temperature, controlled by the thermostat.
- Then, the heated air travels through the hose to the blanket, which inflates.
- The patient contact surface of the blanket permits warm air to escape and move over the patient’s skin, transferring heat to the patient by convection.
- If the temperatures exceed or fall below temperature settings, safety monitoring systems will alarm the caregivers.