Guidewire
- What is guidewire?
- Characteristics of Guidewire
- Components of Guidewire
Guidewire
- A guidewire: a long and flexible, fine metal wire.
- A guidewire as its name shows: helps the interventional cardiologist to guide devices to the diagnostic or treatment site for easier and rapid delivery (navigate vessels).
- Once the tip of the device arrives at the reach a lesion or vessel segment (destination), it acts as a guide that the larger catheter, balloon or stent then fed over it to reach the desired destination.
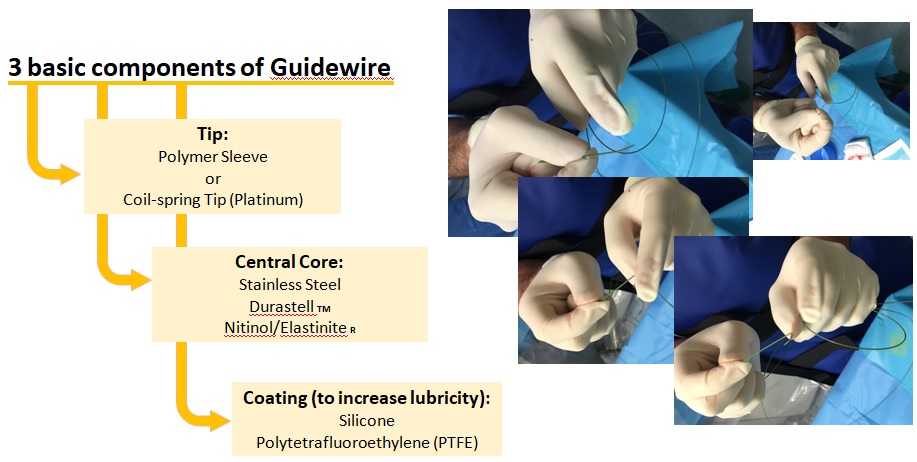
- Constructed of a tightly wound fine wire and a stiff inner core wire
- Sizes: 0.010in to 0.038in diameter
- Length: 50-400 cm
- Outside coated: Teflon, hydrophilic
- Flexible tip: variable length. Allows wire to buckle and avoids dissecting vessel.
- Straight or J-shape end
- Shapeable end: shape memory, easy reshaping

Characteristics of Guidewires
- Pushability: the amount of force needed by the operator at the hub to advance the wire.
(the leading edge of moving forward)
- Steerability: the ability and responsiveness of the wire tip to navigate vessels. (ability of wire to translate rotational movement on the end outside of the patient to the tip inside the patient)
- Torque: the response of the wire to turning and handling by the operator at the hub when navigating vessels. (stiff core transfer 1:1 torque response to distal end.)
- Opacity: level of visibility under fluoroscopic imaging. (radiopacity: nitinol, platinum, gold)
- Elastic flexibility: maneuverability and kink resistant. (nitinol)
3 basic components of Guidewire
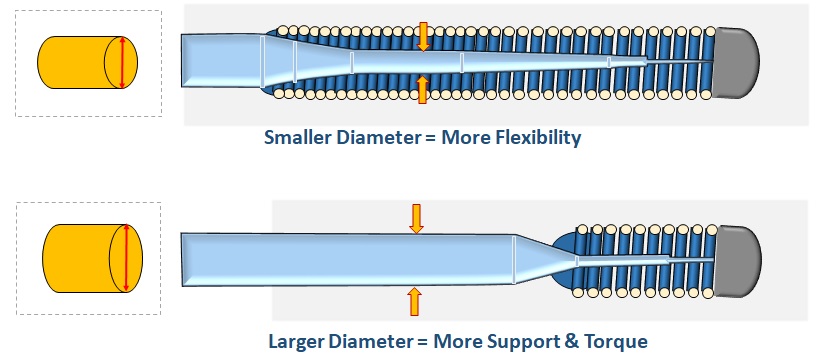
Core Diameter
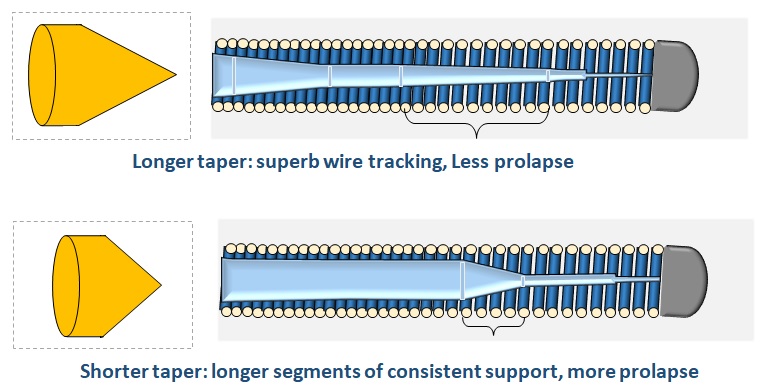
Core Taper