IBP
What is BP?
- Blood pressure (BP) is the force exerted by circulating blood on the walls of blood vessels.
- It constitutes one of the principal vital signs.
- The term blood pressure generally refers to arterial pressure. (The pressure of the circulating blood decreases as blood moves through arteries, arterioles, capillaries, and veins)
- Blood pressure values are reported in millimetres of mercury (mmHg).
- For each heartbeat, blood pressure varies between systolic and diastolic pressures.
- Systolic pressure is a peak pressure in the arteries, which occurs near the beginning of the cardiac cycle when the ventricles are contracting.
- Diastolic pressure is minimum pressure in the arteries, which occurs near the end of the cardiac cycle when the ventricles are filled with blood.
- An example of normal measured values for a resting, healthy adult human is 115-120 mmHg systolic and 75-80 mmHg diastolic (written as 115/75 mmHg).
IBP(IAP) Vs. NIBP(NBP)
Blood pressure monitoring is essential in managing hemo-dynamically unstable critical care patients.
- Invasive measurement from an arterial line (invasive arterial blood pressure [IAP]) is generally considered to be the gold standard
- Automated noninvasive blood pressure systems (NIBP) usually using oscillometric techniques have advantages over invasive arterial lines as they avoid bleeding and infection risk, and can be used outside the care unit.
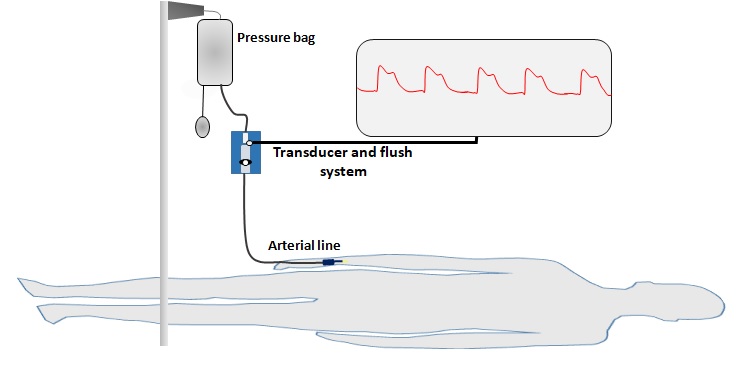
Invasive Arterial Blood Pressure (IAP)
- Arterial blood pressure can be measured directly, accurately, and continuously by inserting a cannula in the radial, brachial, femoral, or dorsalis paedis artery and connecting it to a calibrated transducer, which converts pressure into an electrical signal.
- The arterial cannula also enables repeated blood sampling.
- A pressurized flushing circuit maintains a low flow of saline to keep the cannula patent. The system is calibrated against zero by opening the transducer to air.
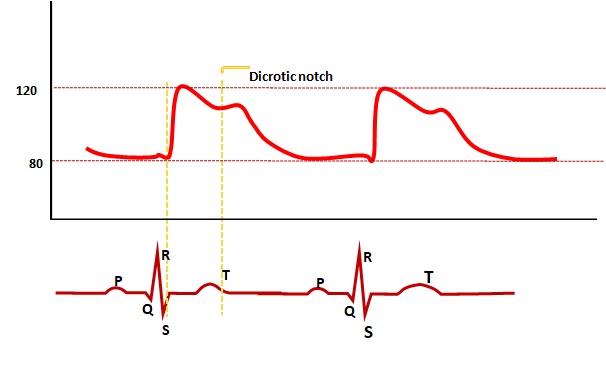
Waveform evaluation
Waveform evaluation is the best method to determine correct placement.
A normal wave form will be:
- within normal blood pressure limits,
- present a characteristic shape and
- synch with the EKG waveform.
- The normal peripheral arterial waveform will display the peak systolic pressure after the QRS.