Infusion Pump
Introduction
- External infusion pumps are medical devices that deliver fluids in large or small volumes, including nutrients and medications (such as insulin or other hormones, antibiotics, chemotherapy drugs, and pain relievers), into a patients body in a controlled manner.
- Infusion pumps have contributed to improvements in patient care, allowing for a greater level of control, accuracy, and precision in drug delivery, and thereby reducing medication errors.
- There are many different types of infusion pumps, which are used for a variety of purposes and in a variety of environments.
- Some infusion pumps are designed mainly for stationary use at a patients bedside. Others, called ambulatory infusion pumps, are designed to be portable or wearable.
Types of Infusion Pumps
Gravity controlled: The simplest and cheapest systems are dial-a-flow/dosiflow, which solely rely on gravity to regulate intravenous infusions. Infusion rate is dependent on pressure difference across the valve i.e. height of fluid or venous pressure/obstruction.
Positive displacement pumps: These provide a positive displacement of fluid with the help of a motor. Positive displacement pumps have either a peristaltic or a piston mechanism.
- Drip rate pumps
- Volumetric pumps
- Syringe pumps
- Multi-channel pumps
- Ambulatory pumps
- Smart infusion pumps
Drip rate pumps
- These pumps use drip sensor attached to administration set to count drops in order to achieve control of infusion rate. The speed of pumping mechanism is under feedback control from a drip sensor/counter.
Volumetric pumps
- These pumps overcome limitations associated with variation in drop size. They use either a piston type action or peristaltic pumping action.
- These pumps are capable of calculating the volume of fluid with the microprocessor based calculations, taking into account the size of the drop produced and the standardized diameter of the tubing.
- Capable of functioning on mains and on rechargeable batteries.
- The pump alarms if bubbles appear in the tube, when infusion is completed, the battery voltage is low and flow line is occluded.
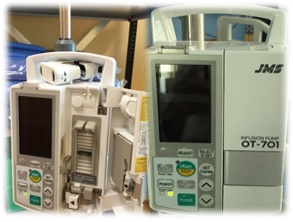
Syringe Pumps
- The most commonly used pumps for the administration of intravenous drugs are positive displacement syringe pumps that utilize a gear reduction mechanism and lead screw.
- These pumps are extremely accurate and have the convenience of not requiring specialized tubing.
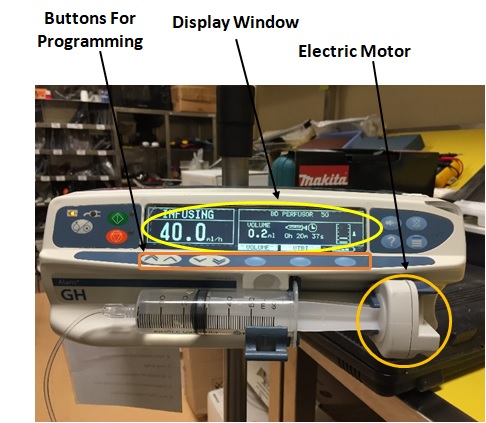

Principles of Operation (Syringe Pumps)
Chassis contains :
- LCD screen
- Alarm to alert user of failures and other issues that need attention
- Power supply
- Memory capabilities
- Records doses, rates, and settings
- Flange clamp sensor
- Determines if syringe flange is present
- Barrel clamp sensor
- Determines if barrel of syringe is present
- Determines size of syringe
- Position sensor
- Determines how far plunger head is from chassis
- Motor and worm gear
- Smoothly moves plunger head outwards
- Unidirectional
- Pyramid shaped reflective counter
- Rotates with motor
- Counts rotations by reflecting light back at a sensor
Multi-channel pumps
- These pumps permit simultaneous administration of 2 or more infusions. However, one potential problem with such a system is the possibility of incompatible mixing.
Ambulatory pumps
- These are pocket size pumps, which use linear peristaltic mechanism and have a fluid container in the form of a small floppy bag or cassette.
- The pumps are designed for users who need to wear them for long periods and they have good alarm and display systems.
Smart Infusion pumps
- These are new generation infusion pumps that incorporate a software that includes a drug library where in hospital-defined drug infusion parameters, such as acceptable concentrations, infusion rates, dosing units, and maximum and minimum loading and maintenance dose bolus limits, for 60 or more medications can be preprogrammed.
