Stent
What is a stent?
Types of stents
Stent
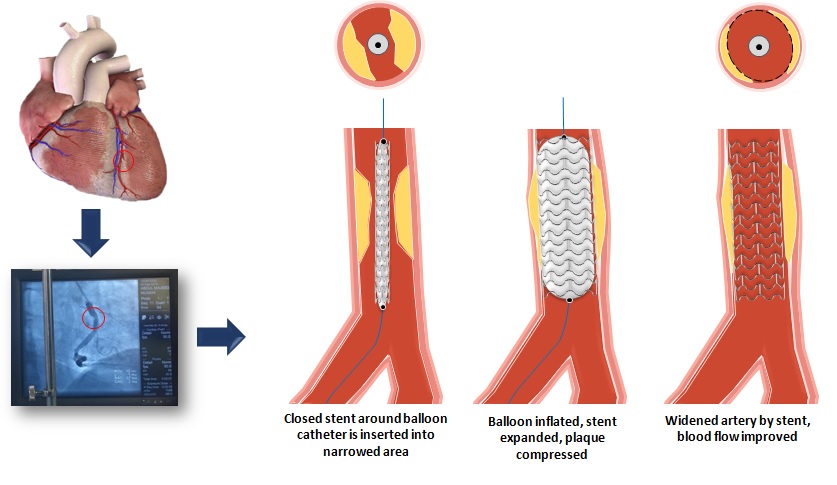
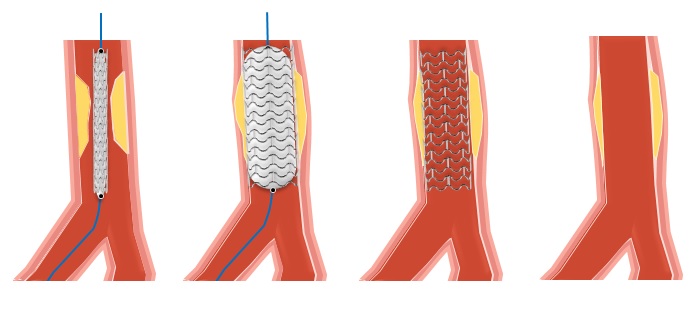
- A stent is a small, metal mesh tube-shaped.
- That is delivered through a catheter to the narrowed artery (site of a blocked passageway) and then permanently embedded within the artery.
- This acts as a tiny scaffold to prop an artery lumen open and prevent it from collapsing or becoming reblocked with plaque.
- The type of stent used will depend on the size of the artery, the location of the blockage and other factors specific to the patients condition, such as whether they have diabetes.
- There are many factors for choosing the right stent for patients such as: the location of blockage, the size of artery, types of plaque or even patients condition (for example whether they have diabetes).
- Stenting helps prevent restenosis(re-narrowing) that usually happens after a few months of balloon angioplasty.

There are currently five types of stents available:
- Dual Therapy Stent (DTS)
- Bioresorbable Vascular Scaffold (BVS)
- Bio-engineered Stent
- Drug Eluting Stent (DES)
- Bare Metal Stent (BMS)
Dual Therapy Stent (DTS)
Dual Therapy Stent (DTS) is the latest type of coronary stent.
- The DTS has a coating for both inside and outside, which reduces the likelihood of blood clots, re-narrowing of the artery, inflammation, promote natural healing and even helps the healthy artery function properly it also helps the healing process of the artery.
- It combines the benefit of DES and bio-engineered stents and is the only stent to contain a drug with active healing technology.
Bioresorbable Vascular Scaffold (BVS)
- The Bio-Vascular Scaffold (BVS) is a fully absorbable stent that is coated with a drug released from a polymer that disappears over time to reduce the likelihood of the artery re-narrowing.
- It’s a drug eluting stent on a dissolvable type of scaffold platform that dissolves and will be overtime by the artery wall.
- Unlike with the DTS, there is no active element to promote artery healing.
Bio-engineered Stent
- Also known as antibody-coated stent.
- It does not contain either a polymer (BVS) or use a drug (DES).
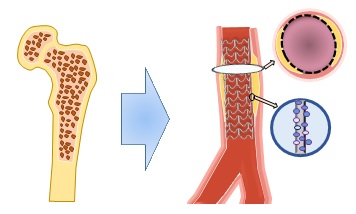
- Bio-engineered Stent is a type of stent that works based on promoting natural healing by helping to speed up the cell lining of the artery (endothelialization).
- Circulating Endothelial Progenitor Cells (EPCs) that made by bone marrow will help speed up the formation of healthy endothelium. the stents surface that contain special antibody will attract EDCs which helps decrease the risk of early and late thrombosis (that caused by blood clots).
Drug Eluting Stent (DES)
- It is a coronary stent coated with medication(antiproliferative drug) that is slowly released (eluted) into the coronary wall for weeks to months after stent implantation to help prevent cell proliferation and restenosis (the growth of scar tissue in the artery lining).
- It also contain polymer coating and helps the artery remain smooth and open, ensuring good blood flow and reduces the chances of the artery re-narrowing.
Limitations:
- Higher chance of blood clots (stent thrombosis).
- Due to a relatively slower healing process, patients implanted with DES must strictly follow their doctors recommendation on drug therapy (DAPT) to help reduce risk of stent thrombosis.
.jpg)
Bare Metal Stent (BMS)
- They act as scaffolding to prop open blood vessels after they are widened with angioplasty.
- Bare metal stents are usually stainless steel without any special coating.
- As the artery heals, tissue grows around the stent, holding it in place.
- Sometimes an overgrowth of scar tissue in the arterial lining increases the risk of re-blockage.