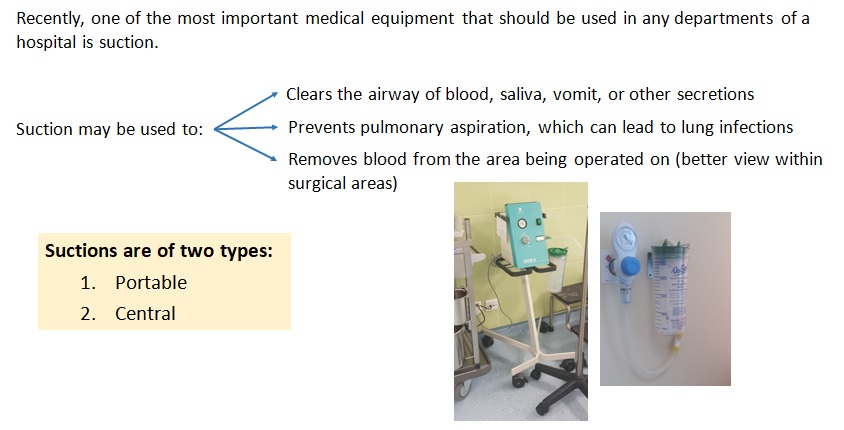
Suction
What is a suction?
Recently, one of the most important medical equipment that should be used in any departments of a hospital is suction.
Central Suction
- In most modern times, The main sources of a vacuum should usually be located in hospitals (the basement of the building). It is a pump and a reservoir.
- Vacuum should be available from wall outlets located throughout of each departments of the building.
- The pump creates a vacuum by emptying a reservoir tank that delivers through connecting pipes to wall outlets in hospital departments (patient care areas).
- Regularly the vacuum pressure restores by engaging a switch when it falls to a predetermined level.
- When it builds back up, the switch disengages and no further vacuum is created.
The rate of flow
The flow rate is determined by three factors:

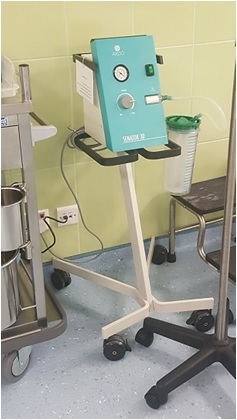
Portable suction
- Can be used to produce vacuum, particularly for hospital areas not served by the wall system (central suction) or those that are not equipped by central suction system.
- Generally, the structure and function of all suctions are the same and they only differ in terms of the system used in vacuum pump.
The main parts of portable suction are:
- Motor
- Vacuum Gauge
- Vacuum Regulator
- Vacuum Pump
- Connective Tubes
- Suction Jar(glass)
- Filter
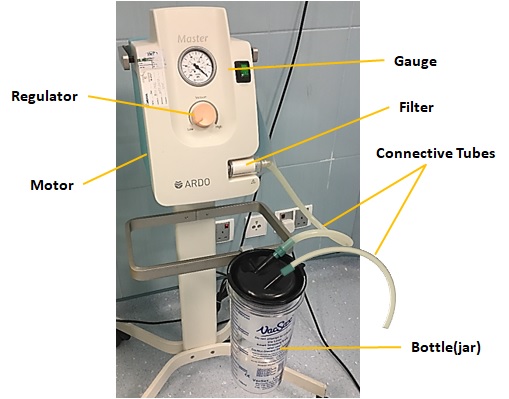
System Component
Motor: Moving vacuum pump which is connected to it. (the oily type has high motor power)
Vacuum Gauge: Showing vacuum power based on two units of measuring the bar and mmHg pressure.
Maximum pressure that could be generated is 1000 mmHg.
Vacuum Regulator: Adjusting the amount of vacuum which is created. (implemented on the body of suction)
Vacuum Pump: creating vacuum inside the pump itself. (this is the most important part of the suction)
It has three models:
- Piston
- Diaphragm
- Oil
System Component…
Connective Tubes: The tubes are connected to two main openings of the pump, one for suction (vacuum) and the other for blow (air) and they are divided into other sub-branches.
Usually, the suction head is connected to disposable sterile tubes.
In operation rooms, based on a surgical place and the surgeons option, different suction tips could be used.
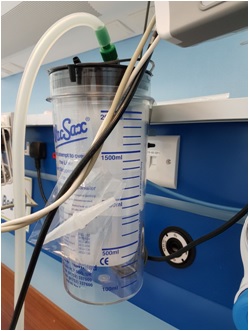
Suction Jar: It has different capacities and two openings, one for connection to a vacuum pump and the other for connection to the suction hose.
For preventing the liquid from entering into the connecting tubes and the pump. it has a control ball(valve) that works as the liquid inside the glass goes up.
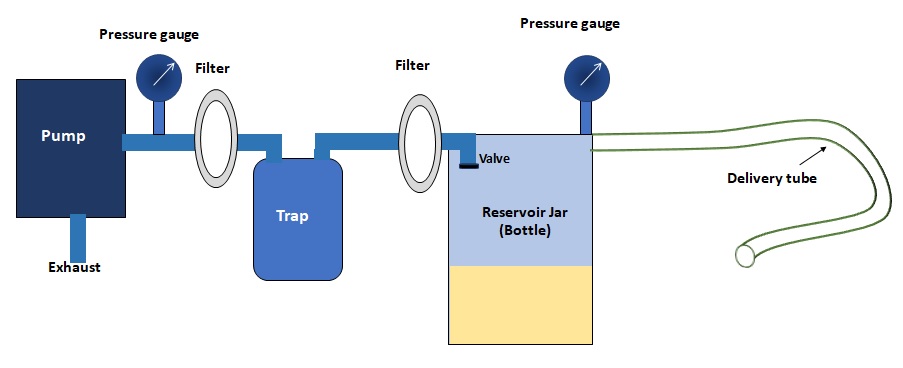
Block Diagram of basic suction