Patient Monitor
Patient Monitor Introduction
- The verb monitor originates from the Latin word monere, which means to remind, advise, or warn.
- Interpret available clinical data to help recognize present or future mishaps or unfavorable system conditions.
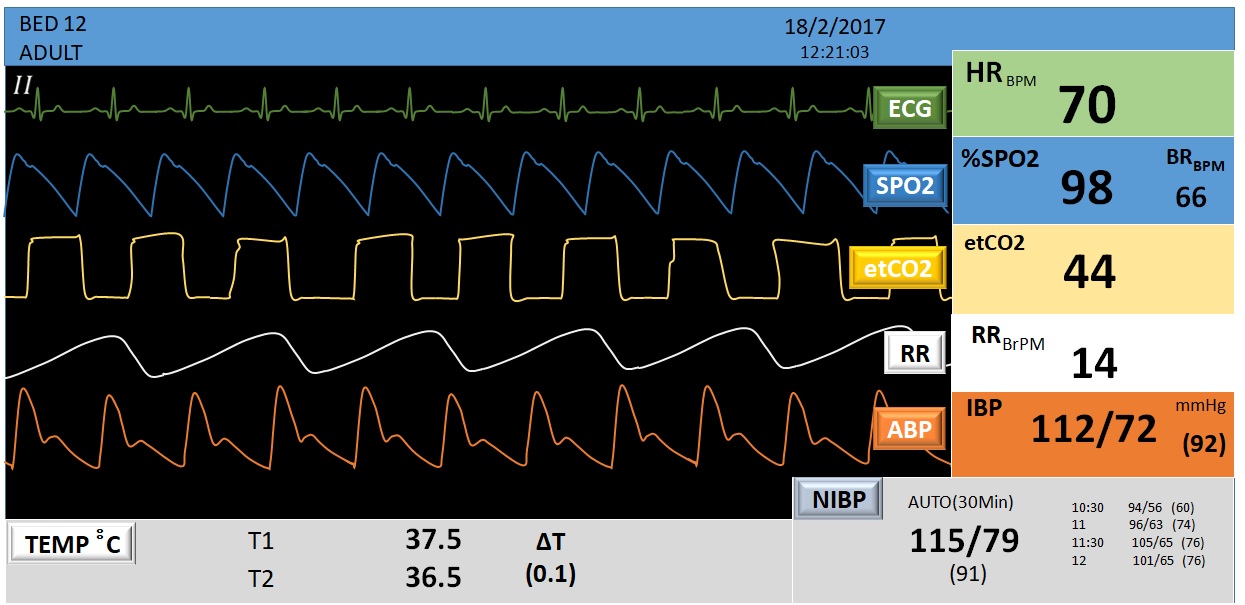
- PMS is a very critical monitoring systems, it is used for monitoring physiological signals including
- Electrocardiograph (ECG)
- Respiration
- Invasive and Non-Invasive Blood Pressure
- Oxygen Saturation in Blood (SpO2)
- Body Temperature
- and etc.
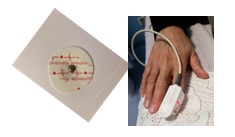
- The multiple sensors and electrodes is used for receiving physiological signals like as: ECG Electrodes, SpO2 Finger Sensor, Blood Pressure Cuff and Temperature Probe to measure the physiological signals.
- Such treatment is best provided in a specialized area of hospital referred to as intensive care unit.(ICU) or critical care unit.(CCU) or even OR(during surgeries).
Classes Of Patient Monitoring System
- In medicine, monitoring is the observation of a disease, condition or one or several medical parameters over time.
Multi-Parameter Patient Monitoring Systems
A multi-parameter PMS is used for multiple critical physiological signs of the patient to transmit the vital information like Electro cardiograph, Respiration Rate, Blood pressure etc.
Single-Parameters Monitoring Systems
The single parameter monitoring system is available for measuring blood pressure of a human body, ECG (Electrocardiograph) monitor, SpO2 (Oxygen Saturation in Blood) monitor and etc.

- In the past, the dominant products manufactured by medical device manufacturers are mainly those for single parameter measurement. Nowadays, a multi-parameter patient monitor is commonly used.
Classification by target parameter
Cardiac monitoring, which generally refers to continuous electrocardiography.
Hemodynamic monitoring, which monitors the blood pressure and blood flow within the circulatory system. (either invasively through an inserted blood pressure transducer assembly, or noninvasively with an inflatable blood pressure cuff)
Body temperature monitoring through an adhesive pad containing a thermoelectric transducer. (it could be invasive or non-invasive)
Respiratory monitoring, such as:
- Pulse oximetry: the saturated percentage of oxygen in the blood, referred to as SpO2, and measured by an infrared finger cuff.
- Capnography: CO2 measurements, referred to as EtCO2 or end-tidal carbon dioxide concentration.
- Respiratory rate: monitoring through a thoracic transducer belt, an ECG channel or via capnography.
Neurological monitoring, such as of intracranial pressure. Also, there are special patient monitors which incorporate the monitoring of brain waves (electroencephalography), gas anesthetic concentrations, bispectral index (BIS), etc. They are usually incorporated into anesthesia machines.
Blood glucose monitoring
Childbirth monitoring
Medical Monitor Components
- A medical monitor or physiological monitor is a medical device used for monitoring. It can consist of one or more sensors, processing components, display devices (called "monitors), as well as communication links for displaying or recording the results elsewhere through a monitoring network.
Sensor
Sensors of medical monitors include biosensors and mechanical sensors.
Translating component
- It is responsible for converting the signals from the sensors to a format that can be shown on the display device or transferred to an external display or recording device.
Display device
- Physiological data are displayed continuously on a CRT, LED or LCD screen as data channels along the time axis. They may be accompanied by numerical readouts of computed parameters on the original data, such as maximum, minimum and average values, pulse and respiratory frequencies and so on.
Communication links
Several models of multi-parameter monitors are networkable.
Other components
A medical monitor can also have the function to produce an alarm (such as using audible signals) to alert the staff when certain criteria are set, such as when some parameter exceeds of falls the level limits.
